Home » Archives for November 2013
Why Cloud Computing?
Benefits of Cloud Computing
If your files are lost, cloud
computing means that you don’t got to worry such a lot. Although you’re disc
drive fails or worse, your pc being purloined, this can be not the tip of your
access to your information. This can bean empowering position to be in, and it
begins to desire cloud technology means that progress can’t be stopped. You’ll
lose onerous drives and servers, however cloud hosting implies that one’s work
can endure. It’s a sound approach for business, and even for private use it
means that storing photos, videos and alternative necessary information isn't any
longer an enormous worry.
It additionally means your IT
employees will spend their time engaged on some very spectacular, participating
comes, instead of endlessly tweaking and maintaining information storage
solutions. Cloud computing means that all of the upkeep is taken care of for
you, and you’ll ne'er need to worry regarding upgrades, staffing servers, or
having your own IT crisis team manage things after they fail (as computers are
used to do). It’s a huge weight off everyone’s shoulders and it means that
you’ll be able to get on with what matters to you and your role.
One of the explanations
individuals additionally go for performing on laptops is that in the first
stages of a business’ lifetime, it’s important to stay prices down till you'll
do one thing property. Housing your servers remotely and having the ability to
drag files from them from multiple devices as you progress could be a powerful
quality to own within the digital business age. This cloud-based skillfulness
means that you’ll be a value effective mean machine that gets things done.
Nothing is additional necessary.
If you’re accustomed the cloud,
then it should be quite tough to imagine however you’d do your job while not
it. Sharing files, keeping everybody up-to-date – several daily tasks whose
cloud-powered speed of completion we have a tendency to hold granted – would be
lots slower while not it, and it’s ne'er attending to want a waste of cash.
Bring some “get up and go” to your work..
Cloud Computing
What is the Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is a part of computing that depends on
sharing computing information resources rather than using Dedicated servers or personal devices to handle
applications over the internet.
In Cloud Computing, the word cloud (also phrased as
"the cloud") is employed as a figure for "the web,"
therefore the phrase cloud computing means that "a variety of
Internet-based computing," wherever totally different services -- like
servers, storage associated applications -- are delivered to an organization's
computers and devices through the net.
Cloud computing is similar to grid computing, a kind of
computing wherever unused process cycles of all computers during a network are
harnesses to resolve issues too intensive for any complete machine.
How Cloud Computing Works
The goal of cloud computing is to use ancient
super-computing or superior computing power, commonly utilized by military and
analysis facilities, to perform tens of trillions of computations per second,
in consumer-oriented applications like monetary portfolios, to deliver personalized
data, to supply information storage or to power massive, immerse PC games.
To do this, cloud computing uses networks of huge teams of
servers’ usually running low-priced client computer technology with specialized
connections to unfold data-processing chores across them. This shared IT
infrastructure contains giant pools of systems that are connected along. Often,
virtualization Techniques are accustomed maximize the ability of cloud
computing.
Cloud Computing Standards
The standards for connecting the PC systems and also the
software system required to create cloud computing work aren't totally outlined
at this time time, going away several corporations to outline their own cloud
computing technologies. Cloud computing systems offered by corporations, like
IBM's "Blue Cloud" technologies as an example, are supported open
standards and open supply software system that link along computers that are
accustomed to deliver internet capabilities like mash-ups or mobile
commerce.
Cloud computing within the Information Center and for tiny
Business.Cloud computing has begun to get mass attractiveness in
company information centers because it allows the information center to work
just like the net through the method of sanctioning computing resources to be
accessed and shared as virtual resources during a secure and scalable manner.
For a little and medium size business (SMB), the advantages
of cloud computing is presently driving adoption within the SMB sector there's
typically an absence of your time and money resources to buy, deploy and
maintain an infrastructure (e.g. the software system, server and storage).
In cloud computing, tiny businesses will access these
resources and expand or shrink services as business wants modification. The
common pay-as-you-go subscription model is intended to let SMBs simply add or
take away services and you sometimes can solely get what you are doing use.
How To Share The Folder
Sharing Folder In Microsoft Windows
Note--For sharing a folder in Microsoft Windows you must be logged on a system via Administrator Account firstly.
1-Create a folder which name you wants, supposed its name is Public on your Computer.
2-Go to Start Button click on Programs, here you will click on Accessories and then pointing out the Windows Explorer.
3-Go to the drive where you make the folder Public and right-click on the folder named Public and then click on sharing option.
4-In folder’s properties option now click on Share this folder.
5-Use the default name for the share and if you wants to change you can but I named this share by-default
And then click Permissions tab.
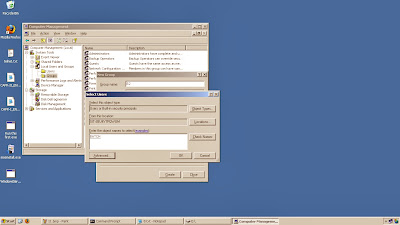
6-At this tab Permissions, click on add option.
7-Now in the option select the Users, Computer or PC and Groups dialog box, Simply click the Authenticated users group and the click on OK.
8-At the Permissions Tab you have to click the Authenticated Users Group Tab.
9-In permissions List, if you wants to Full control simply click the Full Control permission, click on allow and after located the appropriate permissions.
10-Last click on the everyone group and then click remove.
.jpg) |
| Shared Folder |
Note--For sharing a folder in Microsoft Windows you must be logged on a system via Administrator Account firstly.
1-Create a folder which name you wants, supposed its name is Public on your Computer.
2-Go to Start Button click on Programs, here you will click on Accessories and then pointing out the Windows Explorer.
3-Go to the drive where you make the folder Public and right-click on the folder named Public and then click on sharing option.
4-In folder’s properties option now click on Share this folder.
And then click Permissions tab.
6-At this tab Permissions, click on add option.
7-Now in the option select the Users, Computer or PC and Groups dialog box, Simply click the Authenticated users group and the click on OK.
8-At the Permissions Tab you have to click the Authenticated Users Group Tab.
9-In permissions List, if you wants to Full control simply click the Full Control permission, click on allow and after located the appropriate permissions.
10-Last click on the everyone group and then click remove.
What is the Workstation
Workstations
A kind of PC used for engineering applications (CAD/CAM), publication, software system development, and alternative kinds of applications that need a moderate quantity of computing power and comparatively top quality graphics capabilities.
Workstations typically go with an outsizes, high-resolution graphics screen, a minimum of 64 MB (megabytes) of RAM, inbuilt network support, and a graphical interface. Most workstations even have a mass memory device like a hard drive, however a special kind of digital computer, referred to as a disk-less digital computer, comes while not a hard drive. the foremost common operating systems for workstations are operating system and Windows NT.
In terms of computing power, workstations lie between personal computers and minicomputers, the line the road is fuzzy on each ends. High-end personal computers are comparable to low-end workstations. And high-end workstations are like minicomputers.
Like personal computers, most workstations are single-user computers. However, workstations typically usually connected along to create a local-area network, though they\'ll even be used as complete systems.
In networking, workstation refers to any computer connected to a local-area network. It may be a workstation or a private computer.
In another words
It has been said that a bus stops at a bus terminal and a train stops at a railway station, thus what happens at a workstation?
Actually, a digital computer could be a place wherever work gets done. It refers to a PC (and typically the encircling area) that has been organized to perform an exact set of tasks, like pic editing, sound recording, or video production. associate workplace might have many workstations for various functions, which can be appointed to bound workers. as an example, one digital computer is also used for scanning and mercantilism pictures, whereas another is employed for redaction pictures.
Because Workstations typically work along like within the example higher than, they're usually networked along. this enables them to send files back and forth over the network, that is very important for varied varieties of media production. To use another example, a user at a photo-editing digital computer might prepare pictures to be employed in a video clip. Once the pictures are prepared, he might send them to a different user at a Video-Editing Workstation, wherever they're incorporated into the video. Once the video has been place along, the video file is also sent to another user at an audio production workstation wherever the audio recording and alternative sound effects are added .
While workstations are typically a part of a network, they will be standalone machines moreover. Even a computer will be a workstation if it's used for sure varieties of work. thus if you wish to sound professional, successive time you send an e-mail to a disciple from your home computer, you'll be able to let him grasp you're sending it from your home workstation.
.jpg) |
| Workstation-Emperor |
Workstations typically go with an outsizes, high-resolution graphics screen, a minimum of 64 MB (megabytes) of RAM, inbuilt network support, and a graphical interface. Most workstations even have a mass memory device like a hard drive, however a special kind of digital computer, referred to as a disk-less digital computer, comes while not a hard drive. the foremost common operating systems for workstations are operating system and Windows NT.
In terms of computing power, workstations lie between personal computers and minicomputers, the line the road is fuzzy on each ends. High-end personal computers are comparable to low-end workstations. And high-end workstations are like minicomputers.
Like personal computers, most workstations are single-user computers. However, workstations typically usually connected along to create a local-area network, though they\'ll even be used as complete systems.
.jpg) |
| Workstation Networking+Gateway Mode |
In another words
It has been said that a bus stops at a bus terminal and a train stops at a railway station, thus what happens at a workstation?
Actually, a digital computer could be a place wherever work gets done. It refers to a PC (and typically the encircling area) that has been organized to perform an exact set of tasks, like pic editing, sound recording, or video production. associate workplace might have many workstations for various functions, which can be appointed to bound workers. as an example, one digital computer is also used for scanning and mercantilism pictures, whereas another is employed for redaction pictures.
 |
| Workstation Setup for Picture or Image editing |
While workstations are typically a part of a network, they will be standalone machines moreover. Even a computer will be a workstation if it's used for sure varieties of work. thus if you wish to sound professional, successive time you send an e-mail to a disciple from your home computer, you'll be able to let him grasp you're sending it from your home workstation.
Windows Server 2003 Enhancements
Windows Server 2003 Enhancements
Microsoft windows servers every time having with mores of Enhancements but in windows server 2000 family was different types of features and windows server 2003 are different so we talk about the newly launched and advanced server in term of server families is now server 2003.
Active Directory Enhancements one among the most valuable features of Microsoft’s current Windows server OS platform is its ability to support the Active Directory. You’ll see some basic technical info regarding this technology later during this chapter. relating to the administration of the Active Directory, Microsoft has created many enhancements. First, the much-requested feature of drag-and-drop support within the Active Directory body tools has been accessorize. you\'ll conjointly choose multiple objects and simply modification connected properties all right away.
Windows Server 2003 supports another much-requested Active Directory feature:
The ability to rename domains. Since mergers and acquisitions are common within the current business atmosphere, this feature allows systems administrators to adapt their domain names and structures to organizational changes. Note, however, that renaming a domain isn\'t as straightforward as renaming an object like a file; there’s a reasonably extended sequence of steps that has got to be allotted so as for the process to occur successfully.
In terms of to security, resources will currently be simply shared between separate Active Directory forests through the utilization of trust relationships between forests (instead of simply trusts between domains in different forests, as was supported within the Windows 2000 version of Active Directory). this permits for sharing network resources between organizations, and between independent business units or sections of a single organization.
Group Policy Enhancements Through the utilization of group Policy settings, systems administrators are ready to exert additional management over their Windows-based client and server operating systems than ever before. The effective application of group Policy Objects (GPOs) may result in well-managed client pc configurations. This, in turn, can cut back administration prices and may improve the end-user expertise.
One of the challenges of working with group Policy in Windows 2000 Server was the sheer variety of choices and also the some ways during which they might be applied.
This often created it tough to troubleshoot specific policy-related issues. group Policy–related enhancements in Windows Server 2003 embody the group Policy Management Console. This administrative tool (which should be downloaded from Microsoft’s Windows Server 2003 internet site) provides the power to look at GPO-related info throughout the environment employing a single console.
It’s now not necessary to open multiple Active Directory administration tools to search out the correct settings or the reason for a retardant Management Console. This powerful tool includes extra wizards, like the group Policy Modeling Wizard (which permits you to set up for the appliance of GPOs) and therefore the group Policy Results Wizard (which calculated overall effective GPO settings).
Another new feature associated with managing group Policy is that the Resultant Set of Policies tool. As its name implies, this tool may be accustomed verify the particular policy Settings that apply to a selected Active Directory user or PC. The tool goes any by permitting systems administrators to decide on a work mode (which calculates existing policy settings) and a planning mode (which permits for the testing of group Policy settings, before they’re applied). The Resultant Set of Policies console may be wont to determine and set up for the correct application of GPOs.
Internet information Server Enhancements Windows Server 2003 includes IIS 6.0, the most recent version of Microsoft’s web server platform.
IIS includes the subsequent server-side functionality:
¦ HTTP Server wont to serve static web page, as well as method dynamic server-side requests for “active” websites (such as people who are written in ASP, ASP.NET, or different supported languages).
¦ FTP Server provides the flexibility to host and share files over the web or an computer network.
¦ SMTP Server wont to relay e-mail messages inside and outdoors a company.
¦ NNTP Server wont to give access to web and personal newsgroups.
Using the Resultant Set of Policies administrative tool several organizations accept their web servers to produce for communications throughout their organization. IIS 6.0 may be a fully rewritten version of this platform.
Its major new feature is improved method isolation through the utilization of application pools. this permits administrators to separate totally different areas of internet applications from one another, thereby adding protection against application crashes.
The Windows Server 2003 version of IIS additionally provides further options that ought to be useful to Organizations that rely upon it. Overall performance has been improved through the implementation of recent kernel-level routines that scale back performance overhead. Also, administration has been simplified through, for instance, configuration settings that area unit keep in XML files.
Windows Server 2003 additionally ships with intrinsically support for Microsoft’s .NET Framework. This feature permits web and commonplace application developers to simply make the most of Microsoft’s new programming design. though Microsoft states that this can be a significant advantage of Windows Server 2003, it’s necessary to notice that the .NET Framework may be quickly and simply put in on Windows 2000–based computers through a free transfer.
Microsoft windows servers every time having with mores of Enhancements but in windows server 2000 family was different types of features and windows server 2003 are different so we talk about the newly launched and advanced server in term of server families is now server 2003.
Active Directory Enhancements one among the most valuable features of Microsoft’s current Windows server OS platform is its ability to support the Active Directory. You’ll see some basic technical info regarding this technology later during this chapter. relating to the administration of the Active Directory, Microsoft has created many enhancements. First, the much-requested feature of drag-and-drop support within the Active Directory body tools has been accessorize. you\'ll conjointly choose multiple objects and simply modification connected properties all right away.
.jpg) |
| Active Directory Enhancements |
Windows Server 2003 supports another much-requested Active Directory feature:
The ability to rename domains. Since mergers and acquisitions are common within the current business atmosphere, this feature allows systems administrators to adapt their domain names and structures to organizational changes. Note, however, that renaming a domain isn\'t as straightforward as renaming an object like a file; there’s a reasonably extended sequence of steps that has got to be allotted so as for the process to occur successfully.
In terms of to security, resources will currently be simply shared between separate Active Directory forests through the utilization of trust relationships between forests (instead of simply trusts between domains in different forests, as was supported within the Windows 2000 version of Active Directory). this permits for sharing network resources between organizations, and between independent business units or sections of a single organization.
Group Policy Enhancements Through the utilization of group Policy settings, systems administrators are ready to exert additional management over their Windows-based client and server operating systems than ever before. The effective application of group Policy Objects (GPOs) may result in well-managed client pc configurations. This, in turn, can cut back administration prices and may improve the end-user expertise.
One of the challenges of working with group Policy in Windows 2000 Server was the sheer variety of choices and also the some ways during which they might be applied.
This often created it tough to troubleshoot specific policy-related issues. group Policy–related enhancements in Windows Server 2003 embody the group Policy Management Console. This administrative tool (which should be downloaded from Microsoft’s Windows Server 2003 internet site) provides the power to look at GPO-related info throughout the environment employing a single console.
 |
| Group Policy Enhancement |
It’s now not necessary to open multiple Active Directory administration tools to search out the correct settings or the reason for a retardant Management Console. This powerful tool includes extra wizards, like the group Policy Modeling Wizard (which permits you to set up for the appliance of GPOs) and therefore the group Policy Results Wizard (which calculated overall effective GPO settings).
 |
| GPO Full Poster View |
Internet information Server Enhancements Windows Server 2003 includes IIS 6.0, the most recent version of Microsoft’s web server platform.
 |
| IIS Server |
¦ HTTP Server wont to serve static web page, as well as method dynamic server-side requests for “active” websites (such as people who are written in ASP, ASP.NET, or different supported languages).
¦ FTP Server provides the flexibility to host and share files over the web or an computer network.
¦ SMTP Server wont to relay e-mail messages inside and outdoors a company.
¦ NNTP Server wont to give access to web and personal newsgroups.
Using the Resultant Set of Policies administrative tool several organizations accept their web servers to produce for communications throughout their organization. IIS 6.0 may be a fully rewritten version of this platform.
Its major new feature is improved method isolation through the utilization of application pools. this permits administrators to separate totally different areas of internet applications from one another, thereby adding protection against application crashes.
The Windows Server 2003 version of IIS additionally provides further options that ought to be useful to Organizations that rely upon it. Overall performance has been improved through the implementation of recent kernel-level routines that scale back performance overhead. Also, administration has been simplified through, for instance, configuration settings that area unit keep in XML files.
Windows Server 2003 additionally ships with intrinsically support for Microsoft’s .NET Framework. This feature permits web and commonplace application developers to simply make the most of Microsoft’s new programming design. though Microsoft states that this can be a significant advantage of Windows Server 2003, it’s necessary to notice that the .NET Framework may be quickly and simply put in on Windows 2000–based computers through a free transfer.
 |
| Microsoft .NET Framework |
Microsoft Windows Server 2003
Microsoft Windows Server 2003
Many software companies work hard to constantly improve their products, and Microsoft is no exception. Without staying aware of the most recent innovative developments, most programming items will finally fall into lack of definition. Despite the fact that I'm not a Microsoft "insider," I can offer some knowledgeable speculations into what Microsoft's Product were thinking as they decided what would be done to make Windows Server 2003.
A compelling upgrade. Let’s take a glance at however Windows Server 2003 fits in. First, Microsoft is making to follow informed an already in product line the Windows 2000 Server platform. In some ways that, this may be a harder task than fixing an older operating system or application that didn't meet most of its customer’s desires. several organizations have migrated to Windows 2000 Server and are quite proud of that package. In fact, many of Microsoft’s customers (especially several giant organizations) are happy running Windows NT 4.0 Server. So, the challenge for Microsoft is to produce compelling reasons for purchasers to upgrade their server operating systems.
In general, Windows Server 2003 is an progressive improvement over its predecessor, Windows 2000 Server. those that are deploying the operating system can notice that it’s not as massive a shift as was moving from Windows NT 4.0 to the Windows 2000 platform. for instance, the design of the Active Directory remains largely unchanged, though there are many enhancements in performance, dependable, and management options. In fact, Microsoft’s promoting efforts are powerfully targeted on providing compelling reasons for Windows NT 4.0 users to upgrade to Windows Server 2003. Of course, that’s to not say that organizations won’t find it worthy to upgrade from Windows 2000 Server.
Many software companies work hard to constantly improve their products, and Microsoft is no exception. Without staying aware of the most recent innovative developments, most programming items will finally fall into lack of definition. Despite the fact that I'm not a Microsoft "insider," I can offer some knowledgeable speculations into what Microsoft's Product were thinking as they decided what would be done to make Windows Server 2003.
A compelling upgrade. Let’s take a glance at however Windows Server 2003 fits in. First, Microsoft is making to follow informed an already in product line the Windows 2000 Server platform. In some ways that, this may be a harder task than fixing an older operating system or application that didn't meet most of its customer’s desires. several organizations have migrated to Windows 2000 Server and are quite proud of that package. In fact, many of Microsoft’s customers (especially several giant organizations) are happy running Windows NT 4.0 Server. So, the challenge for Microsoft is to produce compelling reasons for purchasers to upgrade their server operating systems.
In general, Windows Server 2003 is an progressive improvement over its predecessor, Windows 2000 Server. those that are deploying the operating system can notice that it’s not as massive a shift as was moving from Windows NT 4.0 to the Windows 2000 platform. for instance, the design of the Active Directory remains largely unchanged, though there are many enhancements in performance, dependable, and management options. In fact, Microsoft’s promoting efforts are powerfully targeted on providing compelling reasons for Windows NT 4.0 users to upgrade to Windows Server 2003. Of course, that’s to not say that organizations won’t find it worthy to upgrade from Windows 2000 Server.
Active Directory Users and Computer Accounts
*Users and Computer Accounts*
A account is utilized to:
*Authentication of client or Machine
*Authorize access to Domain assets
*Audit movements performed utilizing the client or machine account
Active Directory client account empowers a client to log on to computer and domain with an ID that verified and authorized for access to domain assets. Every client who logs on to the Network must have a special client account and watchword. User accounts can also be used as service accounts for some applications.
Normally, Windows 2000 gives predefined client accounts, regarded as Administrator and Guest accounts, that you can use for logging on to a PC that is running Windows 2000. Predefined records are intended to let clients log on to a neighborhood machine and access assets from that PC. Accordingly, these records are composed fundamentally for introductory log on and setup of a local PC. Each one predefined account has an alternate combo of rights and consents. As you may accept, the Administrator account has the most broad rights and authorizations; the Guest record, the minimum.
Despite the fact that helpful, predefined accounts represent a noteworthy issue: If their rights and authorizations are not changed or impaired by a Network administrator.
be utilized by any client or administration to log on to a network by using the Administrator or Guest identity.
To implement the security of client validation and authorization, you must make a individual users account for every user who will partake, by way of the Active Directory Users and Computers utility, on your network. Every User account (including the Administrator and Guest account) can then be added to Windows 2000 group to control the rights and authorizations doled out to the record.
Using accounts and groups that are fitting for your system guarantees that clients logging on to a network might be distinguished and can access just the allowed assets.
Every Active Directory client account has various security-identified choices that figure out how somebody logging on with that specific client account is authenticated on the network
*At first Log-On users must change password.
*User unable to change password.
*Password never expires.
*Password is saved as encrypted clear text.
*User unable to change password.
*Password never expires.
*Password is saved as encrypted clear text.
These options are self-explanatory except for the last one. If you have users logging on
to your Windows 2000 network from Apple computers then user must be select this option
for the accounts.
Create a New account and Password in Windows 2000
In this post we will do the small things but it should be mandatory for the new computer operators or newly aware users or students so lets create the new user account in 2000 family windows!!!!
Create a new user account in windows 2000 should be logged on as an administrator User
To create a new users must be administrator credential!!!
Create a new user account in windows 2000 should be logged on as an administrator User
To create a new users must be administrator credential!!!
1-Click Settings, and afterward click Control Panel
2-In the Control Panel window, click Administrative Tools, and afterward Computer Management.
3-In the Computer Management reassure and under System Tools, extend Local Users and Groups, and afterward click on Users.
Right-click Users and after that click on New User.
Enter account data, for example User Name, Full Name and Password. Put a check beside User should change password at next log on.
Click Close.
Log out of the administrator account by hitting Ctrl-Alt-Del and selecting Log Off. At that point log back in as the new user account.
3-In the Computer Management reassure and under System Tools, extend Local Users and Groups, and afterward click on Users.
Right-click Users and after that click on New User.
Enter account data, for example User Name, Full Name and Password. Put a check beside User should change password at next log on.
Click Close.
Log out of the administrator account by hitting Ctrl-Alt-Del and selecting Log Off. At that point log back in as the new user account.
Active Directory
Active Directory
.jpeg) |
| Windows 2000 based Active Directory structure |
To make this server a new domain controller, you must install Active Directory. A domain controller in a Windows 2000 Server domain is a computer running Windows 2000 Server that manages user access to a network, which includes logons, authentication, and access to the directory and shared resources. The Active Directory Installation wizard configures this server as a domain controller and sets up the DNS if it is not already available on the network. DNS is a system for naming computers and network services; these names are organized into a hierarchy of domains.
TCP/IP networks, such as the Internet, to locate computers and services through user-friendly names. When a user enters a DNS name in an application, DNS services can resolve the name to other information associated with the name, such as an IP address. You can use this wizard for the following scenarios:
No Existing Domain Controller. Sets up your server as the first domain controller on the network. Domain Controller Already on Network. Sets up your server as an additional domain controller, a new child domain, a new domain tree, or a new forest. These entities are defined in the following paragraphs.
An additional domain controller is a Windows 2000 domain controller installed into an existing domain. All domain controllers participate equally in Active Directory replication, but by default the first domain controller installed into a domain is assigned ownership of at least three floating single-master operations. Additional domain controllers installed into an existing domain do not assume ownership of these operations by default.
A child domain is a domain located in the namespace tree directly beneath another domain name (the parent domain). For example, tariq.digitalinfomative.com would be a child domain of the parent domain, digitalinfomative.com. A child domain is also known as a subdomain.
The domain tree is the hierarchical structure that is used to index domain names.Domain trees are similar in purpose and concept to directory trees, which are used by computer filing systems for disk storage. For example, when numerous files are stored on disk, directories can be used to organize the files into logical collections. When a domain tree has one or more branches, each branch can organize domain names used
in the namespace into logical collections.
A forest is a set of one or more trees that do not form a contiguous namespace. All trees in a forest share a common schema, configuration, and global catalog. The trees must trust one another through transitive, bidirectional trust relationships. Unlike a tree, a forest does not need a distinct name. A forest exists as a set of cross-reference objects and trust relationships known to the member trees. Trees in a forest form a hierarchy for the purpose of trust.
NOTE To host Active Directory, you need a partition formatted with the version of NTFS used in Windows 2000.
Configure Your Windows 2000 Server
Configuration of Windows 2000 Server or Advanced 2000 Server:
Thanks to updated management utilities and a slightly enhanced user interface, Windows 2000 Server can be easily configured by using new and improved configuration wizards. If this is your first boot-up of the new operating system, you’ll see the Configure Your Server utility when you start your server, which will facilitate some of the basic configuration techniques. From the flexible interface at the left menu, simply choose the services that you want to run on this server.
We’ll start with Active Directory or initial state of Configuring Windows Server 2000 or Advanced Server 2000
Note If this is not the first boot-up of the new operating system, and you've selected not to be greeted by the configuration utility, you can retrieve it from Start/Programs/Administrative Tools/Configure Your Server. It’s a good idea to do that now so you can follow along here.
Creating a New Domain
To create a new domain, we’ll install Active Directory using the Active Directory Installation wizard, which installs and configures components that provide Active Directory service to network users and computers. In the menu listing of the configuration utility as you can see, click the Active Directory icon to reached at given the screen. At that screen, click Next; then click Start the Active Directory Installation wizard.
Click Next to continue.
Recall that a domain controller is a computer running Windows 2000 Server, which stores directory data and manages user domain interactions, including user logon processes, authentication, and directory searches. Windows 2000 Server domain controllers provide an extension of the capabilities and features provided by Windows NT Server 4.0 domain controllers. A domain can have one or more domain controllers. For high availability and fault tolerance, a small organization using a single local area network
(LAN) might need only one domain with two domain controllers, whereas a large company with many network locations would need one or more domain controllers in each location.
A domain controller in Windows 2000 is also configured using the Active Directory Installation wizard. Active Directory supports multimaster replication of directory data between all domain controllers in the domain. Multimaster replication is an evolution of the primary and backup domain controller (BDC) model used in Windows NT Server 4.0, in which only one server, the primary domain controller (PDC), had a read and-write copy of the directory. Windows 2000 Server multimaster replication synchronizes directory data on each domain controller, ensuring consistency of information over time. Changes in the PDC can be impractical to perform in a multimaster fashion; therefore, only one domain controller, the operations master, accepts requests for such changes. In any Active Directory forest, there are at least five different
operations’ master roles that are assigned to one or more domain controllers.
Let’s create a new domain in Active Directory:
Step 1. Once Active Directory is installed, from the Configure Your Server utility, click Active Directory; from the Active Directory window, choose the domain controller type to create a new domain by selecting Domain controller for a new domain; then click Next.
Step 2. In the next window, choose to create a new domain tree by selecting Create
a new Domain Tree and then click Next.
Step 3. Next, choose to create a New Forest of domain trees by selecting Create a
new forest of domain trees; then click Next.
Step 4. Specify a name for the new domain by typing the full DNS name then click Next.
Step 5. Specify the Network Basic Input/Output System (NetBIOS) name for the new domain. Earlier versions of Windows will use this to identify the new domain. Click Next.
Step 6. In the next window, specify in the fields provided the locations of the Active Directory database and log, either by accepting the default locations or by clicking Browse to find new ones. Click Next to continue.
Step 7. In the next window, you must specify the folder to be shared as the system volume. The Sysvol folder stores the server’s copy of the domain’s public files. Either accept the default location or click Browse to find a new one. Click Next to continue.
Step 8. DNS must be installed. If DNS is not available; the wizard will configure it for the new domain. Select Yes to install DNS and then click Next.
Step 9. In the next window, you must select the default permissions for user and group objects. You do this by selecting Permissions compatible with Pre-Windows 2000 servers over Permissions compatible only with Windows 2000 servers to be compatible with our NT server programs. Click Next to continue.
Step 10. specify an administrator password to use when starting the computer in restore mode; then click Next.
Step 11. In the next window, review and confirm the previously selected options; then click Next. The wizard will configure Active Directory, as shown
Step 12. In the next window, click Finish to close the wizard; then click Restart
Now to reboot the server.
I thinks it goes to Interesting but it completed and from Now you’re ready to learn how to manage Active Directory.
Thanks to updated management utilities and a slightly enhanced user interface, Windows 2000 Server can be easily configured by using new and improved configuration wizards. If this is your first boot-up of the new operating system, you’ll see the Configure Your Server utility when you start your server, which will facilitate some of the basic configuration techniques. From the flexible interface at the left menu, simply choose the services that you want to run on this server.
We’ll start with Active Directory or initial state of Configuring Windows Server 2000 or Advanced Server 2000
.jpg) |
| Windows 2000 Configure Your Server |
Creating a New Domain
To create a new domain, we’ll install Active Directory using the Active Directory Installation wizard, which installs and configures components that provide Active Directory service to network users and computers. In the menu listing of the configuration utility as you can see, click the Active Directory icon to reached at given the screen. At that screen, click Next; then click Start the Active Directory Installation wizard.
Click Next to continue.
 |
| Active Directory wizard front end |
Recall that a domain controller is a computer running Windows 2000 Server, which stores directory data and manages user domain interactions, including user logon processes, authentication, and directory searches. Windows 2000 Server domain controllers provide an extension of the capabilities and features provided by Windows NT Server 4.0 domain controllers. A domain can have one or more domain controllers. For high availability and fault tolerance, a small organization using a single local area network
(LAN) might need only one domain with two domain controllers, whereas a large company with many network locations would need one or more domain controllers in each location.
A domain controller in Windows 2000 is also configured using the Active Directory Installation wizard. Active Directory supports multimaster replication of directory data between all domain controllers in the domain. Multimaster replication is an evolution of the primary and backup domain controller (BDC) model used in Windows NT Server 4.0, in which only one server, the primary domain controller (PDC), had a read and-write copy of the directory. Windows 2000 Server multimaster replication synchronizes directory data on each domain controller, ensuring consistency of information over time. Changes in the PDC can be impractical to perform in a multimaster fashion; therefore, only one domain controller, the operations master, accepts requests for such changes. In any Active Directory forest, there are at least five different
operations’ master roles that are assigned to one or more domain controllers.
 |
| Starting the Active Directory wizard |
Step 1. Once Active Directory is installed, from the Configure Your Server utility, click Active Directory; from the Active Directory window, choose the domain controller type to create a new domain by selecting Domain controller for a new domain; then click Next.
Step 2. In the next window, choose to create a new domain tree by selecting Create
a new Domain Tree and then click Next.
Step 3. Next, choose to create a New Forest of domain trees by selecting Create a
new forest of domain trees; then click Next.
Step 4. Specify a name for the new domain by typing the full DNS name then click Next.
Step 5. Specify the Network Basic Input/Output System (NetBIOS) name for the new domain. Earlier versions of Windows will use this to identify the new domain. Click Next.
Step 6. In the next window, specify in the fields provided the locations of the Active Directory database and log, either by accepting the default locations or by clicking Browse to find new ones. Click Next to continue.
Step 7. In the next window, you must specify the folder to be shared as the system volume. The Sysvol folder stores the server’s copy of the domain’s public files. Either accept the default location or click Browse to find a new one. Click Next to continue.
Step 8. DNS must be installed. If DNS is not available; the wizard will configure it for the new domain. Select Yes to install DNS and then click Next.
 |
| Specifying a new domain |
Step 10. specify an administrator password to use when starting the computer in restore mode; then click Next.
Step 11. In the next window, review and confirm the previously selected options; then click Next. The wizard will configure Active Directory, as shown
Step 12. In the next window, click Finish to close the wizard; then click Restart
Now to reboot the server.
I thinks it goes to Interesting but it completed and from Now you’re ready to learn how to manage Active Directory.
Windows 2000/Windows 2000 Server Installation and Configuration
Basic Windows 2000/Windows 2000 Server Installation and Configuration
This Post steps you through the installation process of your windows 2000 family server or windows and it should be important for new users that how we can make a server 2000 and how we can make all of these roles and managing of their roles so let’s to implements the server 2000 family server or windows!!!!
Launching Windows 2000 Server
To launch Windows 2000 Server, power up the system with the Microsoft Windows
2000 Server CD in your primary CD-ROM drive. Be sure that your system’s Setup
specifies the primary boot process, starting with CD-ROM. Then follow these steps:
Step 1. In the Welcome to Setup screen, you are given three options:
■■ Press Enter to set up Windows 2000.
■■ Press R to repair a Windows 2000 installation.
■■ Press F3 to quit Setup without installing Windows 2000.
In this case, press Enter to continue with the installation process.
Step 2. License Agreement. View the entire Windows 2000 Licensing Agreement
by pressing Page Down. At the end of the agreement, press F8 to accept its terms and continue.
Step 3. Location Selection and Drive Format. Select an installation location for
Windows. In this step, you may create/delete active hard drive partitions; after
which, select the partition to which you want to install the operating system,
and press Enter. By pressing Enter, you may now choose to format the partition
by using the File Allocation Table (FAT) system or the NT File System (NTFS). In
this case, select NTFS.
Step 4. Setup will copy the installation files to the selected partition. When
Setup is finished, press Enter to restart the system and continue with the
installation.
Step 5. Windows 2000 Setup Wizard. Windows 2000 Server Setup wizard will
complete the installation process. Press Next to acknowledge. The wizard will
detect and install devices on the system.
Step 6. Regional Settings. You can customize Windows 2000 Server for different
regions and settings. For local settings, click Customize and set the current local,
time, date, and currency. Click OK to accept the changes. For keyboard settings,
click Customize and select your keyboard properties. Click OK to accept the settings.
Click Next when you are ready to continue with the installation.
Step 7. Personalizing Windows 2000. Type your full name and the name of your
company or organization; then click Next.
Step 8. Licensing Mode. Based on Microsoft’s definitions as they are extracted
here, choose either the per-seat or the per-server licensing type; then click Next.
PER-SEAT LICENSING A per-seat license associates a Client Access License with
a specific computer or “seat.” Client computers are allowed access to any Windows NT
Server or Windows NT Server, Enterprise Edition on the network, as long as each
client machine is licensed with the appropriate Client Access License. The per-seat
mode is most economical in distributed computing environments where multiple
servers within an organization provide services to clients, such as a company that uses
Windows NT Server for file and print services.
PER-SERVER LICENSING A per-server license associates a Client Access License
with a particular server. This alternative allows concurrent-use licensing: If customers
decide to use the server in per-server mode, they must have at least as many Client
Access Licenses dedicated to that server to accommodate the maximum number of
clients that will connect to that server at any one point in time. The server assigns
Client Access Licenses temporarily to client computers; there is no permanent Client
Access License association with a specific client machine. If a network environment has
multiple servers, then each server in per-server mode must have at least as many Client
Access Licenses dedicated to it as the maximum number of clients that will connect to
it at any one point in time. Under this option, the customer designates the number of
client access licenses that apply to the server during setup. The per-server mode is most
economical in single-server, occasional-use, or specialty-use server solutions (with
multiple concurrent connections). Some examples include Remote Access Service solutions,
CD-ROM servers, or the initial server of a planned larger deployment.
Step 9. Server Name and Password. Enter a name for the computer and the
administrator password (up to 14 characters); then click Next.
Step 10. Windows 2000 Components. To add or remove a component, click the
checkbox. Ashaded box means that only part of the component will be installed.
To see what’s included in a component, click Details. You may elect to install services
such as DNS from the Components window; however, for our purposes
here we’ll accept the default settings for accessories, utilities, and services
(including Internet International Server [IIS]) and then click Next to continue.
Step 11. Date and Time. Verify the correct date, time, and time zone; click Next
to confirm and accept.
Step 12. Networking Settings. The setup wizard will install the networking
components. Choose whether to use typical (auto install of common services) or
custom settings (manually configure networking components). For now, select
Typical settings and click Next.
Step 13. Workgroup or Computer Domain. Select to make this computer a
member of a domain or workgroup. Click Next to continue.
Step 14. Installing Components and Completing Setup. The setup wizard will
install your component selections (this may take several minutes) and will also
perform final tasks, such as registering components, saving settings, and
removing temporary files.
Step 15. Click Finish to complete the setup wizard. Remove the CD-ROM; then
restart the computer.
Step 16. Logging in. After you restart the system, you’ll have to log in with the
administrative password configured during the setup process. For security, the
password will display as asterisks as you type it in.
So now we can log in to Windows server 2000 and ready to create some effective which had not done earlier and here installation of windows server 2000 is complete so on next post we will talk about the managing and administration of the server 2000 and making domain included with Active directory!!!!
This Post steps you through the installation process of your windows 2000 family server or windows and it should be important for new users that how we can make a server 2000 and how we can make all of these roles and managing of their roles so let’s to implements the server 2000 family server or windows!!!!
Launching Windows 2000 Server
To launch Windows 2000 Server, power up the system with the Microsoft Windows
2000 Server CD in your primary CD-ROM drive. Be sure that your system’s Setup
specifies the primary boot process, starting with CD-ROM. Then follow these steps:
Step 1. In the Welcome to Setup screen, you are given three options:
■■ Press Enter to set up Windows 2000.
■■ Press R to repair a Windows 2000 installation.
■■ Press F3 to quit Setup without installing Windows 2000.
In this case, press Enter to continue with the installation process.
Step 2. License Agreement. View the entire Windows 2000 Licensing Agreement
by pressing Page Down. At the end of the agreement, press F8 to accept its terms and continue.
Step 3. Location Selection and Drive Format. Select an installation location for
Windows. In this step, you may create/delete active hard drive partitions; after
which, select the partition to which you want to install the operating system,
and press Enter. By pressing Enter, you may now choose to format the partition
by using the File Allocation Table (FAT) system or the NT File System (NTFS). In
this case, select NTFS.
Step 4. Setup will copy the installation files to the selected partition. When
Setup is finished, press Enter to restart the system and continue with the
installation.
Step 5. Windows 2000 Setup Wizard. Windows 2000 Server Setup wizard will
complete the installation process. Press Next to acknowledge. The wizard will
detect and install devices on the system.
Step 6. Regional Settings. You can customize Windows 2000 Server for different
regions and settings. For local settings, click Customize and set the current local,
time, date, and currency. Click OK to accept the changes. For keyboard settings,
click Customize and select your keyboard properties. Click OK to accept the settings.
Click Next when you are ready to continue with the installation.
Step 7. Personalizing Windows 2000. Type your full name and the name of your
company or organization; then click Next.
Step 8. Licensing Mode. Based on Microsoft’s definitions as they are extracted
here, choose either the per-seat or the per-server licensing type; then click Next.
PER-SEAT LICENSING A per-seat license associates a Client Access License with
a specific computer or “seat.” Client computers are allowed access to any Windows NT
Server or Windows NT Server, Enterprise Edition on the network, as long as each
client machine is licensed with the appropriate Client Access License. The per-seat
mode is most economical in distributed computing environments where multiple
servers within an organization provide services to clients, such as a company that uses
Windows NT Server for file and print services.
PER-SERVER LICENSING A per-server license associates a Client Access License
with a particular server. This alternative allows concurrent-use licensing: If customers
decide to use the server in per-server mode, they must have at least as many Client
Access Licenses dedicated to that server to accommodate the maximum number of
clients that will connect to that server at any one point in time. The server assigns
Client Access Licenses temporarily to client computers; there is no permanent Client
Access License association with a specific client machine. If a network environment has
multiple servers, then each server in per-server mode must have at least as many Client
Access Licenses dedicated to it as the maximum number of clients that will connect to
it at any one point in time. Under this option, the customer designates the number of
client access licenses that apply to the server during setup. The per-server mode is most
economical in single-server, occasional-use, or specialty-use server solutions (with
multiple concurrent connections). Some examples include Remote Access Service solutions,
CD-ROM servers, or the initial server of a planned larger deployment.
Step 9. Server Name and Password. Enter a name for the computer and the
administrator password (up to 14 characters); then click Next.
Step 10. Windows 2000 Components. To add or remove a component, click the
checkbox. Ashaded box means that only part of the component will be installed.
To see what’s included in a component, click Details. You may elect to install services
such as DNS from the Components window; however, for our purposes
here we’ll accept the default settings for accessories, utilities, and services
(including Internet International Server [IIS]) and then click Next to continue.
Step 11. Date and Time. Verify the correct date, time, and time zone; click Next
to confirm and accept.
Step 12. Networking Settings. The setup wizard will install the networking
components. Choose whether to use typical (auto install of common services) or
custom settings (manually configure networking components). For now, select
Typical settings and click Next.
Step 13. Workgroup or Computer Domain. Select to make this computer a
member of a domain or workgroup. Click Next to continue.
Step 14. Installing Components and Completing Setup. The setup wizard will
install your component selections (this may take several minutes) and will also
perform final tasks, such as registering components, saving settings, and
removing temporary files.
Step 15. Click Finish to complete the setup wizard. Remove the CD-ROM; then
restart the computer.
Step 16. Logging in. After you restart the system, you’ll have to log in with the
administrative password configured during the setup process. For security, the
password will display as asterisks as you type it in.
So now we can log in to Windows server 2000 and ready to create some effective which had not done earlier and here installation of windows server 2000 is complete so on next post we will talk about the managing and administration of the server 2000 and making domain included with Active directory!!!!
Labels
- Cloud Computing (2)
- Servers (2)
- Windows Server 2000 Family (5)
- Windows Server 2003 Family (2)
- Workstations (3)
Archives
Subscribe via email
Popular Posts
-
Sharing Folder In Microsoft Windows Shared Folder Note --For sharing a folder in Microsoft Windows you must be logged on a system via...
-
How To Manage Your Social Media Monitoring Your Social-Media The nature of “social media...

.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)



.jpg)




















.jpg)

.jpeg)
